In the quest for a sustainable future, understanding our energy consumption is crucial. As we transition to renewable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a leading contender. However, to be truly ‘solar savvy’, we must first understand our energy consumption patterns, particularly in relation to household appliances.
In today’s world, household appliances are not just a luxury but a necessity. From refrigerators preserving our food to air conditioners maintaining a comfortable living environment, these appliances play a pivotal role in our daily lives. However, with the increasing reliance on these devices, it’s essential to understand their energy consumption patterns, particularly their peak consumption levels measured in Watts. This understanding can help us manage our energy usage more efficiently, leading to significant savings on electricity bills and contributing to a more sustainable environment.
This article will delve into the energy consumption of household appliances and how we can optimise their use for a solar-powered future.
Understanding Energy Consumption in Household Appliances
Household appliances account for a significant portion of our energy use. According to data from YourHome, the appliances that use the largest amount of energy in an average Australian home are heating and cooling systems (40%), water heaters (21%), and other appliances, including refrigeration, cooking, and lighting (33%). Standby power, the energy used by appliances when they are switched off but still plugged in, accounts for about 6% of household energy use.
Energy consumption of an appliance refers to the amount of electrical energy it uses to function. It’s typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), a unit that represents the energy consumption of a 1,000-watt appliance running for one hour. However, the power consumption of appliances can vary significantly based on their type, model, and usage patterns.
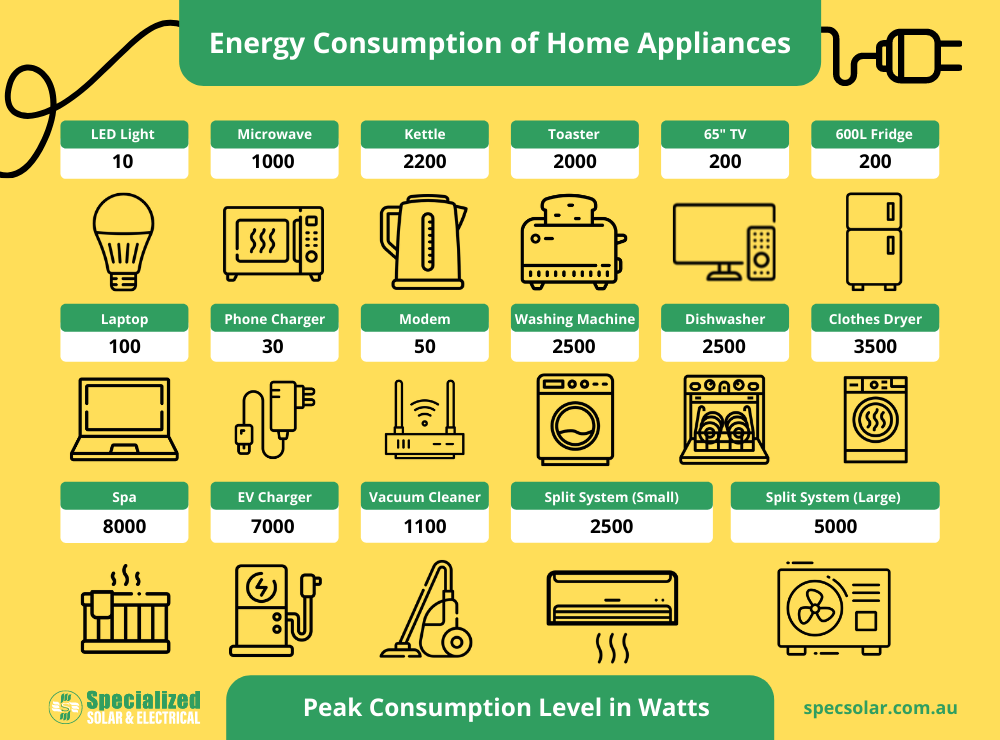
Peak Consumption Levels:
Peak consumption refers to the maximum amount of power an appliance draws at any given moment, measured in Watts (W). This is often when the appliance is operating at its highest setting or during startup. For instance, an air conditioner may draw more power when it first turns on and is working to cool down a room quickly.
Here are some common household appliances and their approximate peak consumption levels:
- Refrigerator: A standard refrigerator can have a peak power consumption between 100-400 Watts. The peak usually occurs when the compressor kicks in to cool the interior.
- Air Conditioner: A central air conditioning unit can consume around 3,500 Watts at peak, while a window unit can consume between 500-1,500 Watts, depending on the size and model.
- Washing Machine: A washing machine can have a peak power consumption of around 500-1,500 Watts, depending on the model and the cycle chosen.
- Dishwasher: Dishwashers can have a peak power consumption of around 1,200-2,400 Watts, with the higher end typically associated with the drying cycle.
- Microwave: A microwave oven can consume between 600-1,200 Watts at peak, depending on the power level chosen for cooking.
- Television: A modern LED television can consume between 30-100 Watts at peak, while older CRT models can consume up to 150 Watts.
- Computer: A desktop computer can consume between 100-800 Watts at peak, depending on the hardware and the tasks it’s performing.
- LED Lights: LED lights are highly energy-efficient. A typical LED bulb can have a peak power consumption of around 10-20 Watts, depending on its brightness.
- Toaster: A toaster can have a peak power consumption of around 800-1,500 Watts, depending on the model and the toasting level.
- Kettle: An electric kettle can consume between 1,000-1,500 Watts at peak, usually when it’s heating the water to boiling point.
- Vacuum Cleaner: A vacuum cleaner can have a peak power consumption of around 500-1,500 Watts, depending on the model and the suction power.
- Dryer: A clothes dryer can consume between 1,800-5,000 Watts at peak, with the higher end typically associated with high heat settings and larger models.
Harnessing solar energy for household use is a significant step towards sustainable living. However, to truly reap the benefits of this renewable energy source, it’s crucial to understand the optimal usage of household appliances. By aligning the operation of these devices with solar production, you can lower your electricity bills and increase self-consumption of the solar energy you generate. Here are some strategies for efficient use of your heating and cooling systems, water heaters, and other appliances.
Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating and cooling systems are the largest energy consumers in most homes. These systems are essential for maintaining a comfortable living environment, but they can also be energy hogs. To reduce their energy consumption, consider using energy-efficient models, maintaining your systems regularly, and using them only when necessary. For example, instead of using air conditioning, you could open windows to allow a natural breeze in, or use fans which consume less energy. Here are some other strategies:
- Time of Use: Operate your heating and cooling systems during the day when your solar panels are producing the most energy. This is typically between 9 AM and 3 PM.
- Thermostat Settings: Set your thermostat to a comfortable but energy-efficient temperature when you’re home and awake. Consider increasing (for cooling) or decreasing (for heating) the temperature settings when you’re away or asleep.
- Pre-Cooling or Pre-Heating: During peak solar production hours, pre-cool or pre-heat your home. This strategy allows your system to run less during expensive peak utility hours, using more of your solar energy instead.
Water Heaters
Water heaters are the second-largest energy consumers in the home. To reduce their energy consumption and optimise efficiency, consider using electric heat pump systems. Electric heat pumps are a modern and highly efficient alternative to traditional water heaters.
- Electric Heat Pumps: Consider investing in an electric heat pump system for your water heating needs. These systems use electricity to transfer heat from the surrounding air to heat the water, resulting in significant energy savings throughout the year. Electric heat pumps provide savings and efficiency all year round. They can be likened to your own ‘thermal battery,’ allowing you to utilise renewable energy for water heating before investing in a battery storage system (BESS).
- Time of Use: Optimise its energy usage by using hot water during the day when your solar system is generating power. This includes activities like showering, running the dishwasher, or doing laundry.
Other Appliances
Other appliances, including refrigeration, cooking, and lighting, account for a significant portion of household energy use. To reduce their energy consumption, consider using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when not in use, and unplugging appliances when they’re not in use to reduce standby power consumption.
- Daytime Use: Run high-energy appliances like the washing machine, dryer, and dishwasher during the day when your solar panels are generating the most electricity.
- Energy-Efficient Models: Consider investing in energy-efficient appliances, which can operate effectively with less power.
- Smart Appliances: Smart appliances can be programmed to run at specific times, allowing you to align their operation with peak solar production hours.
- Battery Storage: Consider investing in a solar battery storage system. It stores excess solar energy produced during the day for use during the evening or during power outages, increasing your self-consumption and reducing reliance on the grid.
Becoming Solar Savvy
Now that we understand where our energy is going, the consumption levels of appliances and strategies for efficient use and self-consumption, we can take steps to become more ‘solar savvy’. This means optimising our energy use to make the most of solar power, to consume as much as possible before it goes to the grid.
Maximise Your Solar Panels by Choosing the Right Inverters
Solar panels offer an excellent means to tap into the sun’s energy for electricity generation. Whether mounted on rooftops or other sun-drenched locations, they can substantially contribute to a household’s power requirements. The inverter, however, is the linchpin of this system, rendering the panels ineffective without it. It’s the heart, the soul, and the brain of the operation. Prioritising a high-efficiency inverter that enables comprehensive monitoring via a single app is crucial to mastering the art of being ‘Solar Savvy’.
Use Energy-Efficient Appliances
Energy-efficient appliances use less electricity, making them ideal for homes powered by solar energy. Look for appliances with high energy ratings – the more stars, the more energy-efficient the appliance.

Choose an appliance with a high star rating
Source: energyrating.gov.au
Monitor Your Energy Use
Monitoring your energy use can help you identify areas where you can save energy. Consider using a home energy monitor to track your energy consumption in real-time.
Use Energy at Off-Peak Times
Solar energy is most abundant during the day. By using energy-intensive appliances during the day, you can make the most of your solar power.
In Conclusion
Becoming ‘solar savvy’ involves understanding our energy consumption and taking steps to optimise it for solar power. By doing so, we can reduce our reliance on traditional energy sources and move towards a more sustainable future.
Understanding the peak power consumption of household appliances can be a crucial step towards efficient energy management. By being aware of when and how these devices consume energy, we can make informed decisions about their usage, leading to potential energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint. Remember, every bit of energy saved contributes to a more sustainable and energy-efficient world. Consumption over feed in, is the goal all day long.
Get in touch
Are you ready to take control of your energy consumption and make the switch to solar? Our team of solar experts is here to guide you on your journey towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient lifestyle. We’ll help you understand your unique energy needs and answer all your questions to ensure you choose the best solar power system for your home.
Don’t wait to start your journey towards energy independence and sustainability. Reach out to us today for a free consultation and learn more about how understanding your energy consumption can lead to significant savings and a smaller carbon footprint. Let’s work together to create a brighter, greener future.















